LED street lights
Production “Industrial LED luminaires/PendantLED luminaires/LEDfloodlights/StreetLED luminaires
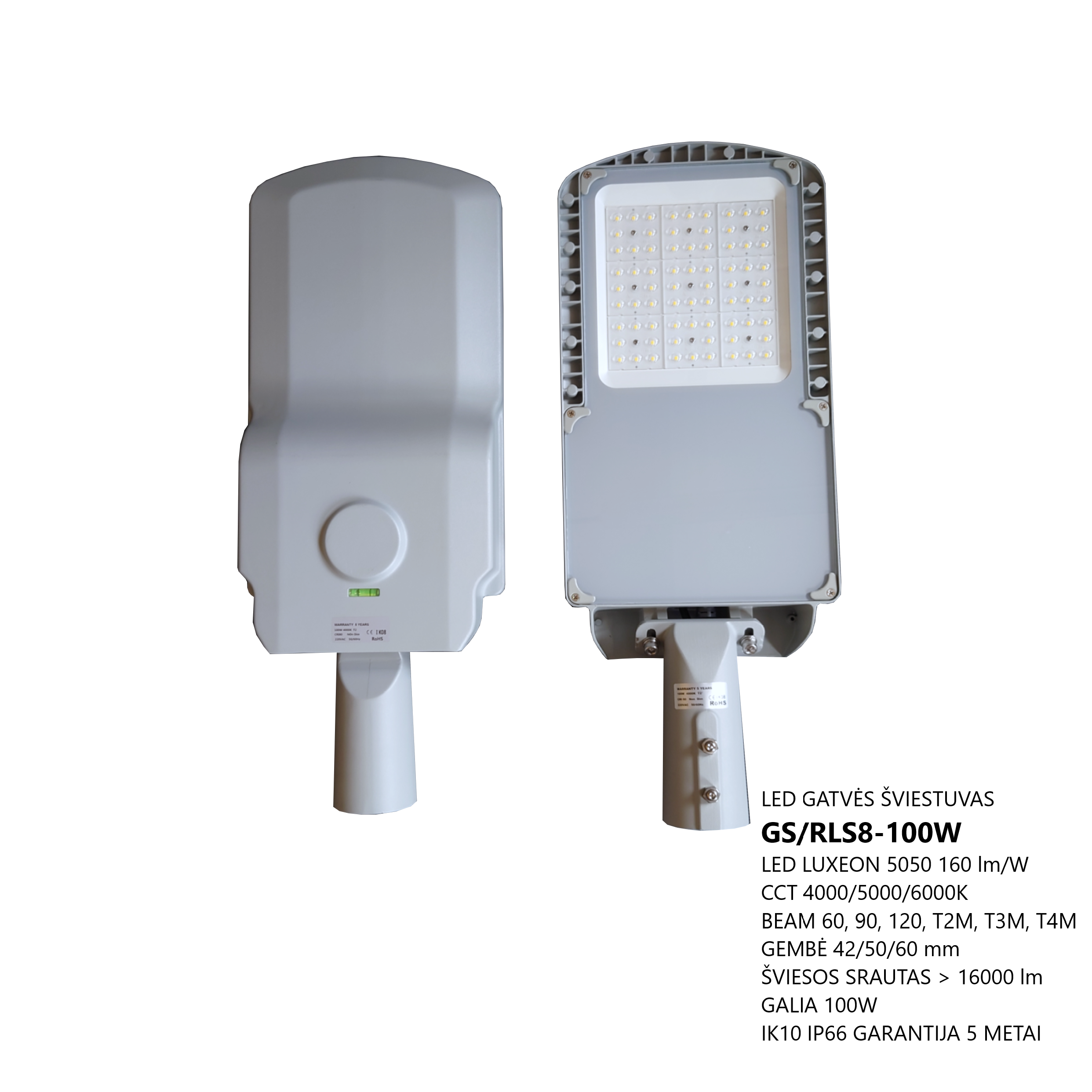
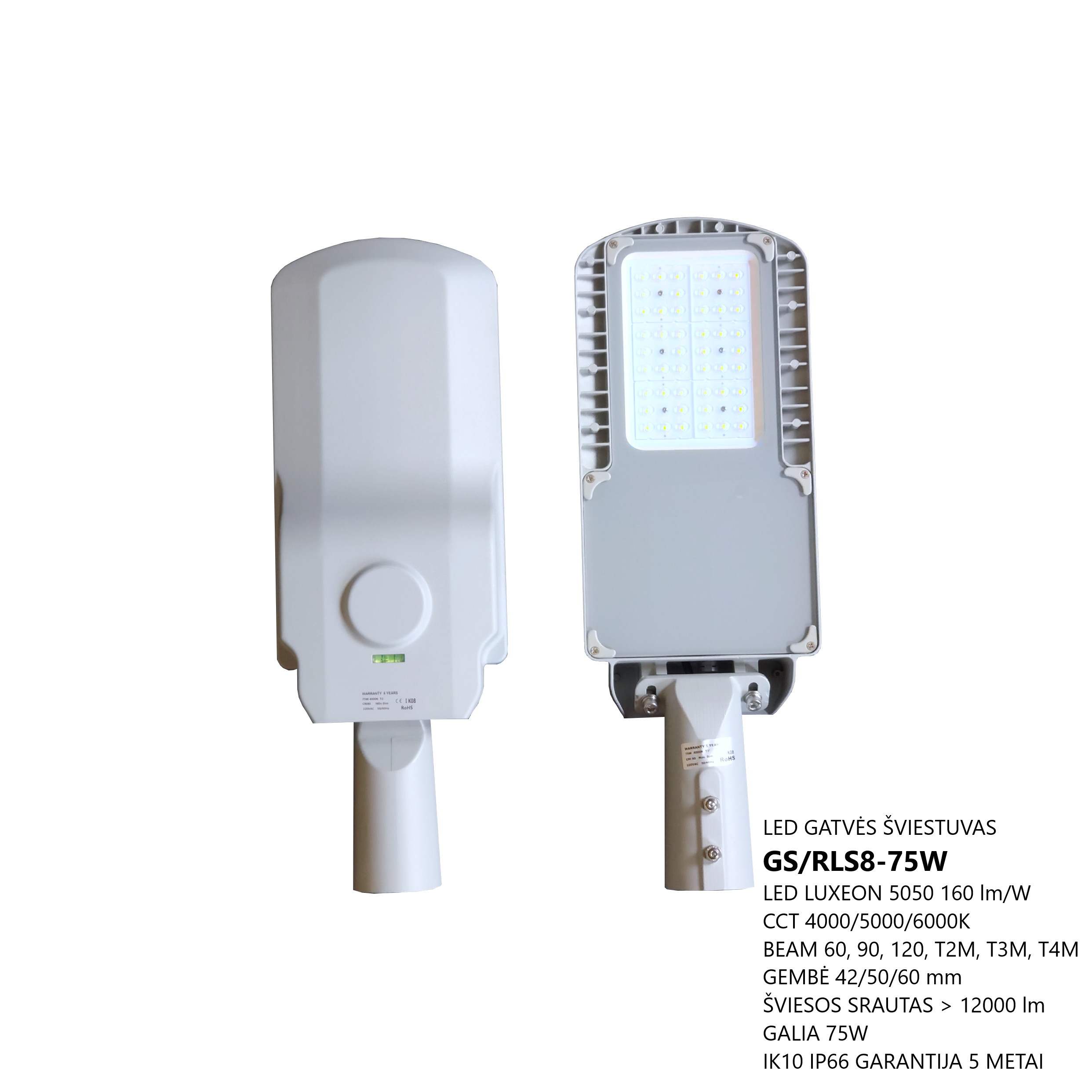
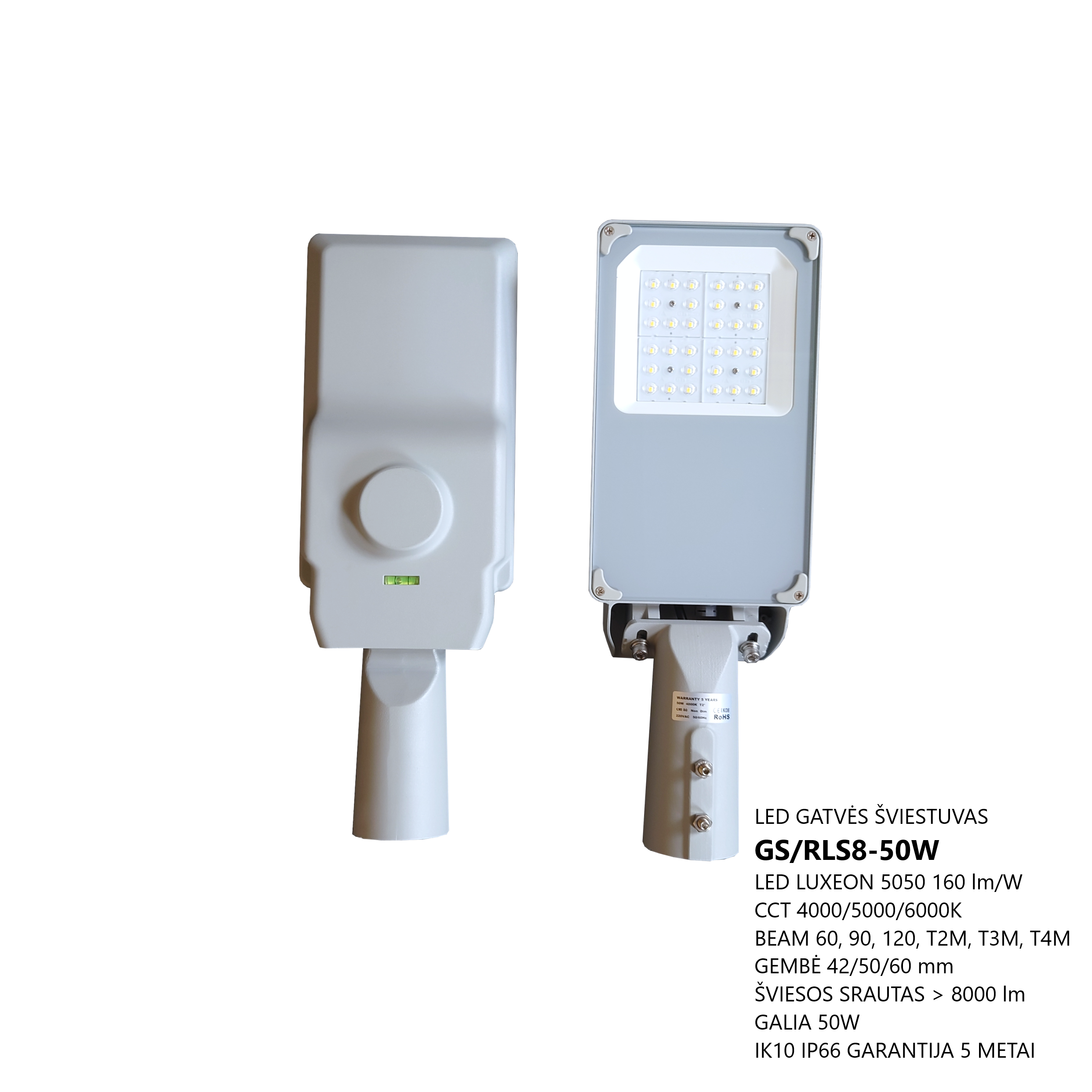
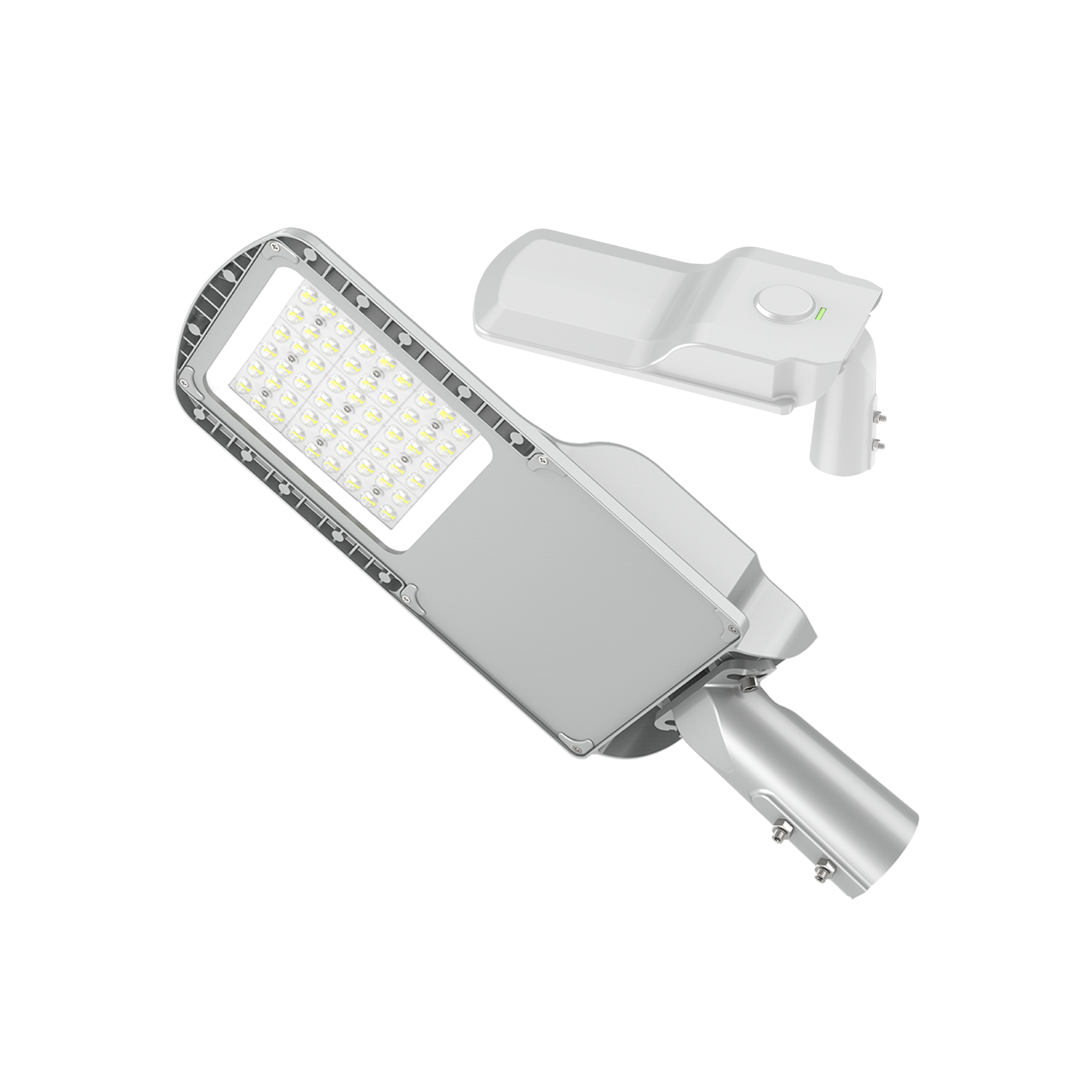
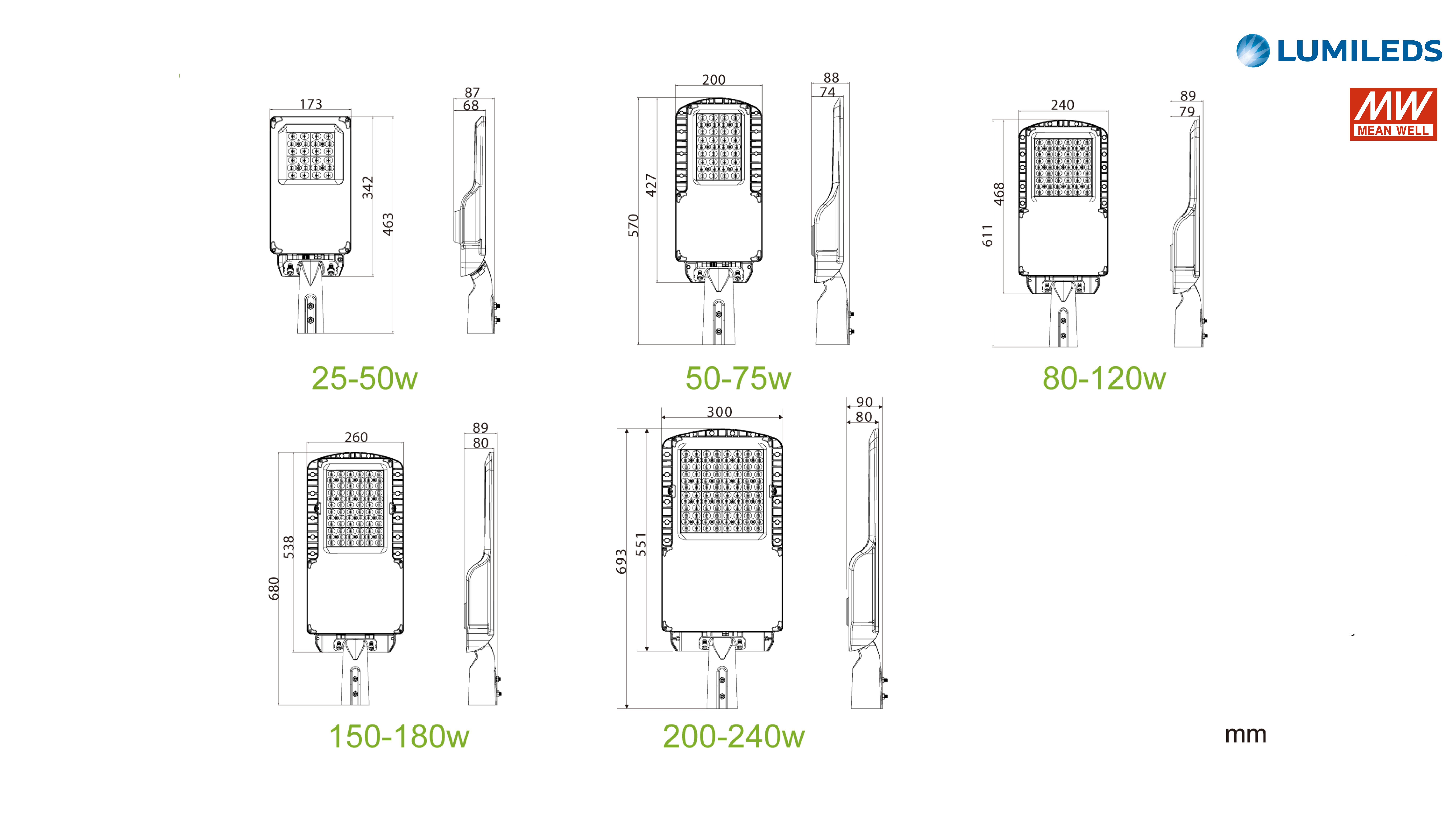
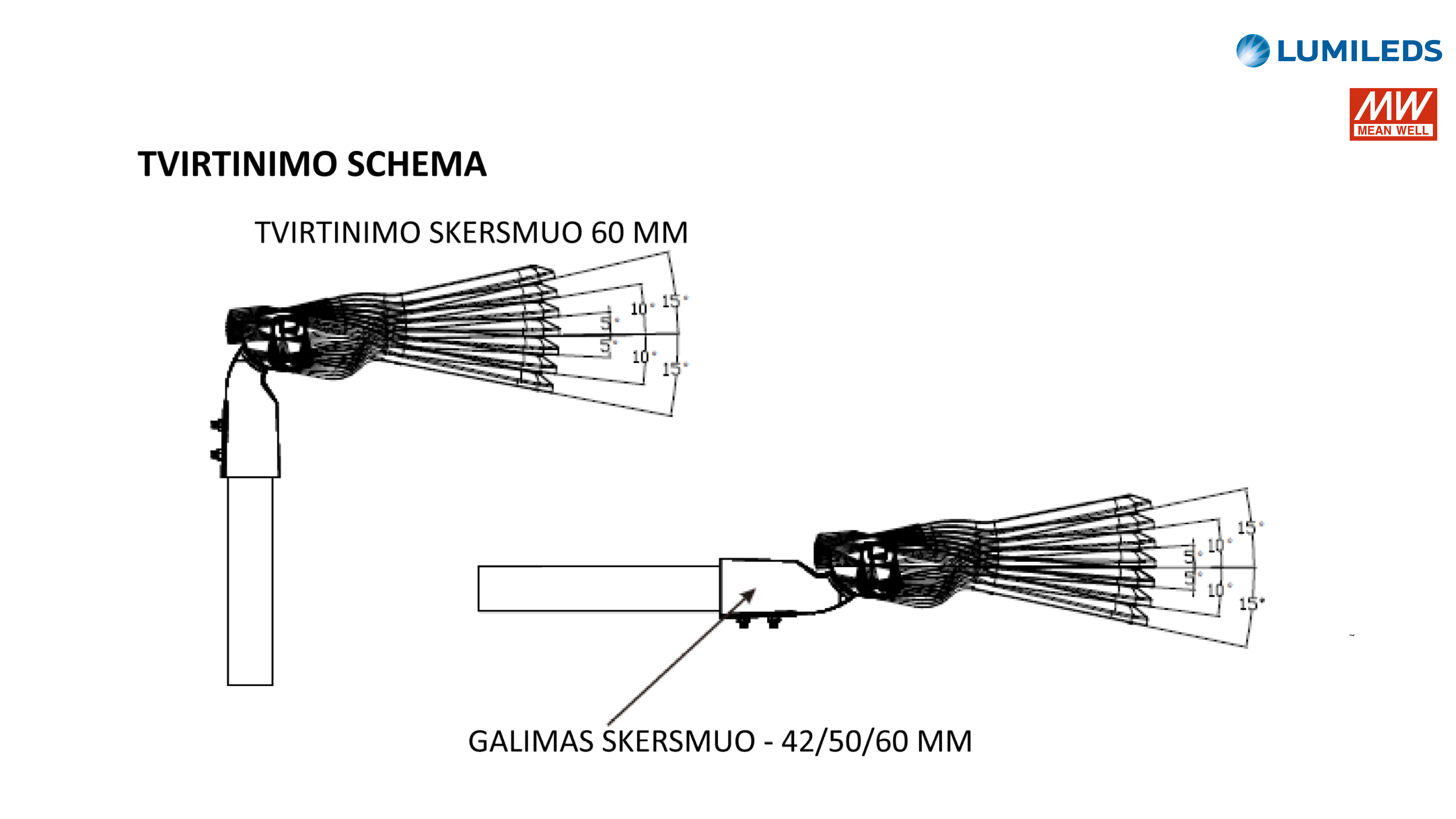
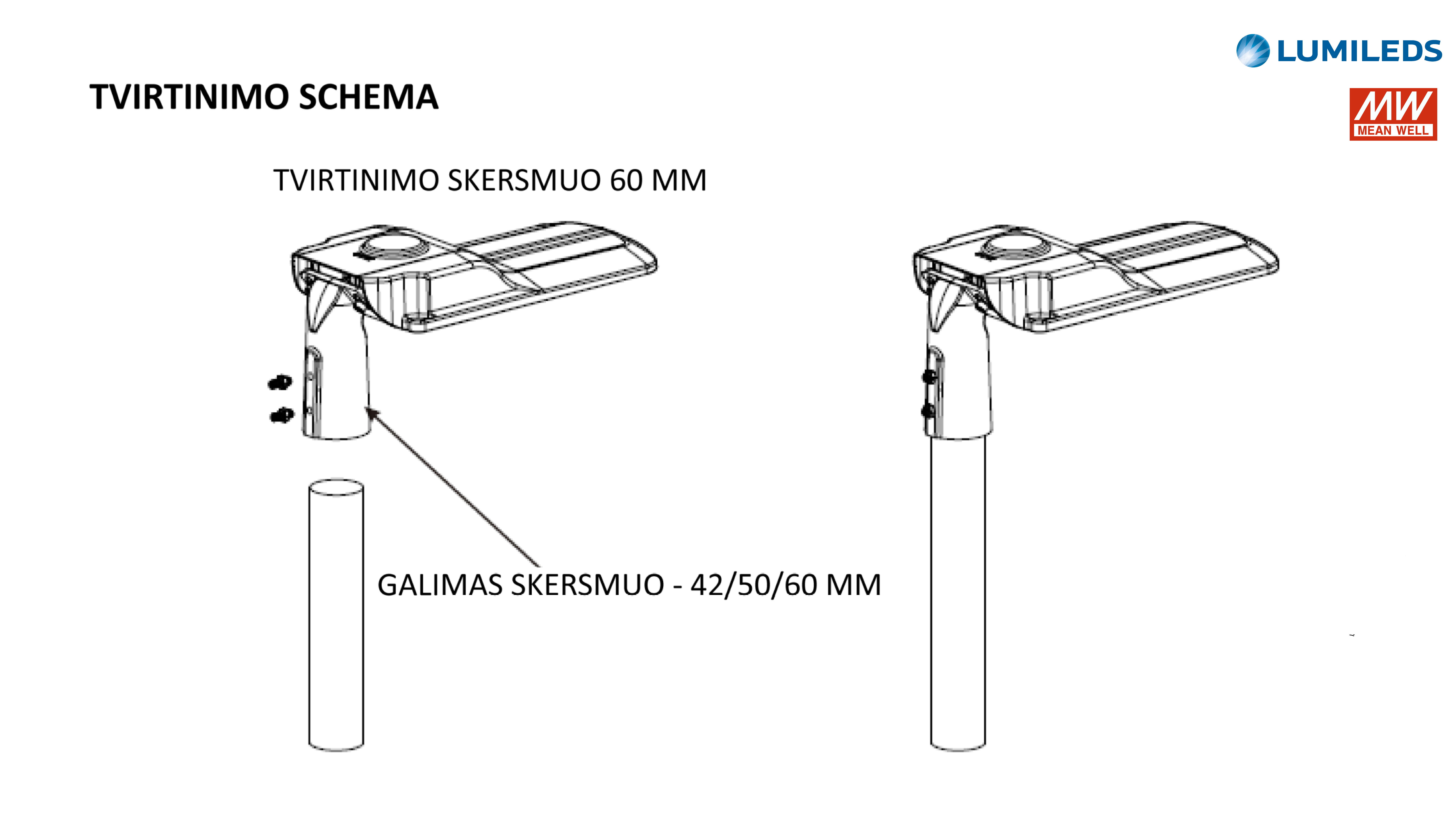
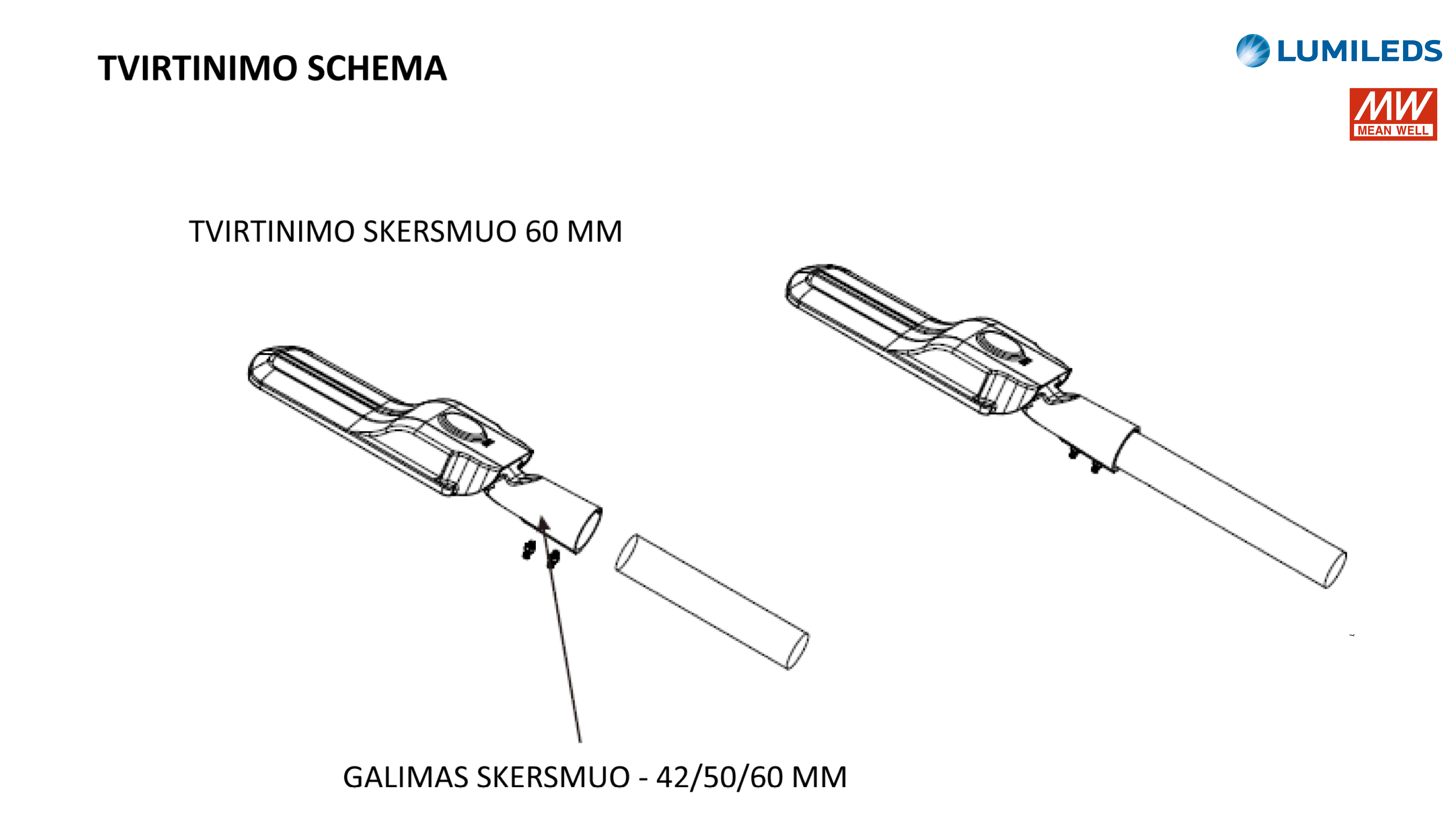
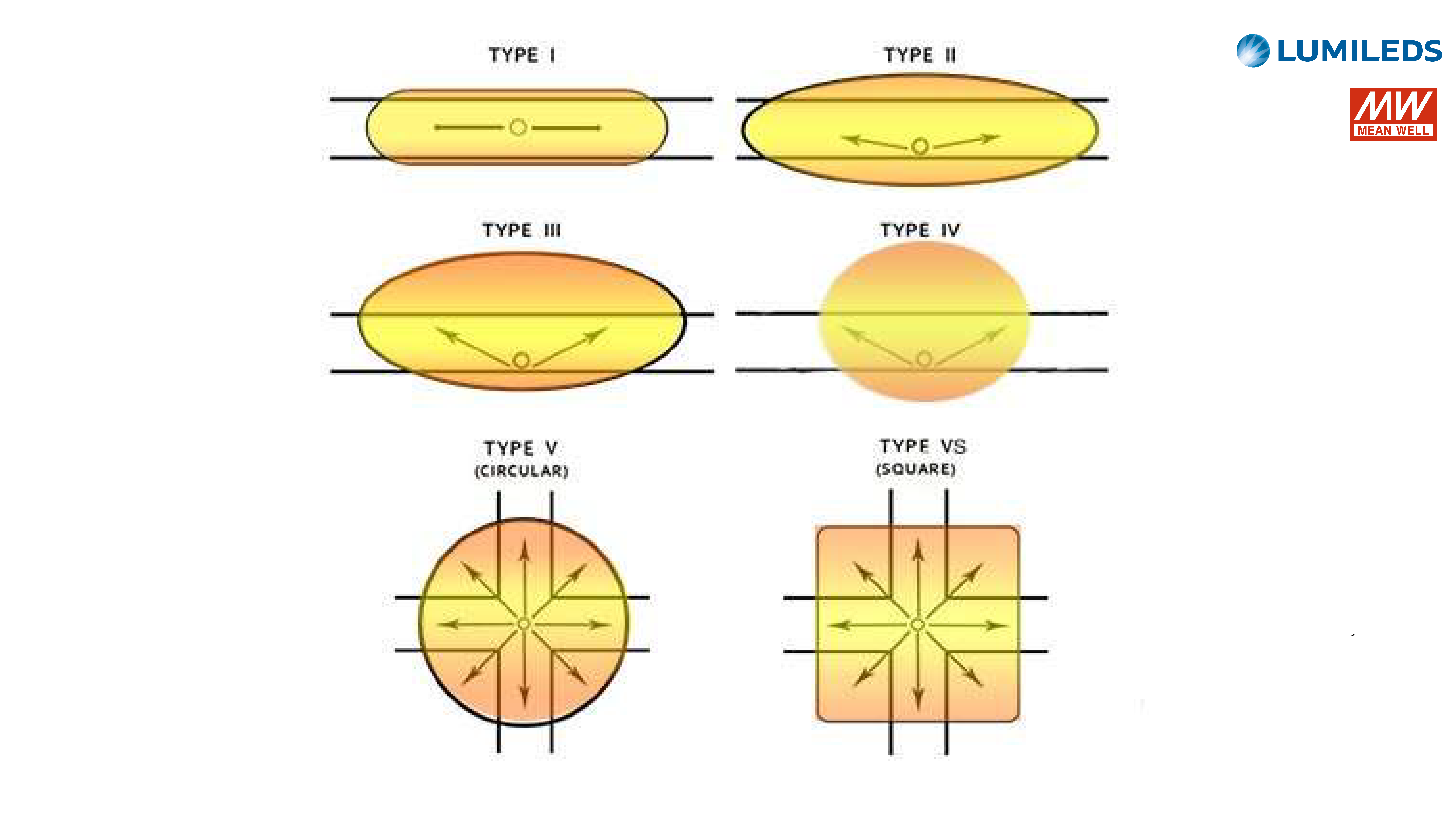
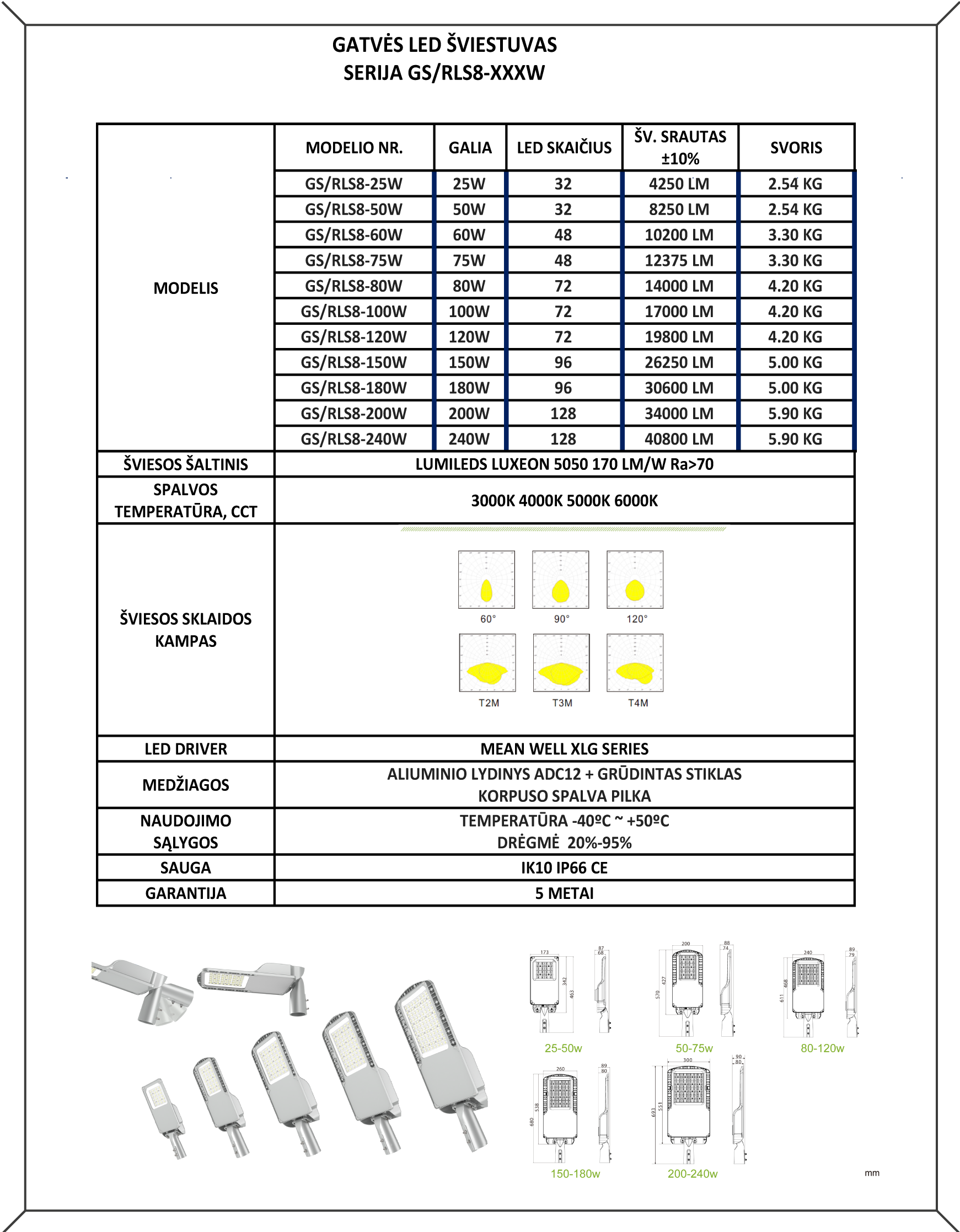
The GS/RLS8-XXXW LED street luminaires are designed for outdoor areas and squares. LED driver Mean Well, LED light source – LUXEON 5050, colour temperature (CCT): 3000K/4000K/5000K/5000K/6000K, beam angle – 60°/90°/120°/T2M/T3M/T4M, power from 25W to 240W, resistance – IK10 IP66. LED luminaires are subject to strict quality and reliability requirements and come with a 5-year warranty.
USE
Outdoor area lighting, outdoor parking lot lighting, loading bay lighting, petrol station lighting, lighting of other premises and areas.
LED STREET LIGHT GS/RLS8-XXXW
Warnings, precautions and instructions for use
INSTALLATION WORK MAY ONLY BE CARRIED OUT BY A SUITABLY QUALIFIED PERSON WITH A HAZARDOUS WORK PERMIT
DO NOT COVER THE BACK OF THE LUMINAIRE. DO NOT PLACE THE POWER SUPPLY ON THE BACK OF THE LUMINAIRE
- The luminaire shall be Class I for protection against electric shock and shall be earthed
- The mechanical suspension system of the luminaire shall be able to support 5 times the weight
- The power cord will not be replaced if it is damaged and the appliance is faulty
- The power supply of the luminaire shall not be covered by any material
- Make sure the luminaire and power supply are in good working order before installation
- The luminaire must not be squeezed, thrown or broken
- Do not install near heat sources
- It is mandatory to switch off the automatic voltage switches before installing the luminaire
USEFUL INFORMATION
WHAT IS AN LED?
A light-emitting diode is a semiconductor device that directly converts an electric current into a light beam. In English, a light emitting diode is called a light emitting diode or LED. A LED consists of a semiconductor crystal, a housing with contact wires and an optical system.

DOES THIS MEAN THAT THE MORE CURRENT THAT PASSES THROUGH AN LED, THE BRIGHTER IT SHINES?
Of course it is. The higher the current, the more electrons and holes enter the recombination zone per unit time. However, the current cannot be increased indefinitely because the internal resistance of the semiconductor and the p-n junction will cause the diode to overheat and fail.
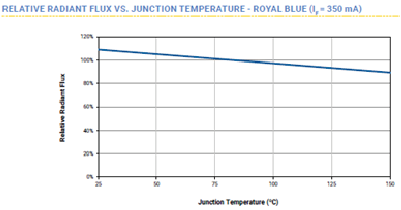
HOW DOES AN LED REACT TO A TEMPERATURE RISE?
As regards the temperature of the LED, it is necessary to distinguish between the temperature at the crystal surface and the temperature at the p-n junction. Lifetime depends on the former, luminous flux on the latter. In general, the brightness of an LED decreases with increasing p-n junction temperature because the internal quantum efficiency decreases due to the influence of vibrations in the crystal lattice. That’s why good heat dissipation is so important.
WHY IS IT NECESSARY TO STABILISE THE CURRENT SUPPLIED TO THE LED?
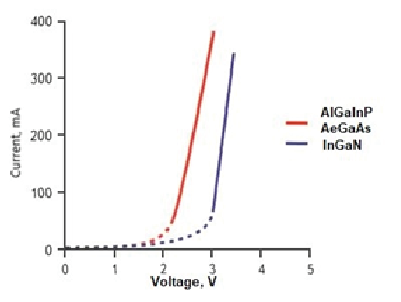
As can be seen from the figure, in the operating modes, the current depends exponentially on the voltage, and small changes in voltage cause large changes in current. As the luminous flux is directly proportional to the current, the brightness of the LED is also unstable. The current must therefore be stabilised. In addition, if the current exceeds the permissible limit, overheating of the LED can accelerate its ageing. An LED converter (LED driver in English terminology) stabilises the current flowing through an LED.
WHAT DETERMINES THE LIFETIME OF AN LED?
LEDs are said to be particularly durable. But it isn’t. The more current that passes through an LED, the higher its temperature and the faster it ages. Ageing is primarily manifested by a decrease in brightness. When the brightness drops by 30% or half, the LED must be replaced. The ageing of an LED is not only related to a decrease in brightness but also to a change in colour. There are currently no standards to quantify the colour change of LEDs as they age and compare them with other sources.
Cost-effectiveness and durability…
One of the advantages of LEDs is their longevity. These light sources have a lifetime of 100 000 hours, which is 10-12 years of continuous operation. By comparison, neon and fluorescent lamps have a maximum lifetime of 10,000 hours. At the same time, a light module using fluorescent lamps will need to be replaced 8-10 times and incandescent lamps will need to be “switched on” again 30 to 40 times. Using LED modules can reduce energy consumption by up to 87%!
Convenience …
The LED module is a multi-component structure with an unpretentious wiring scheme. For example, in a circuit of fifty LEDs, one or two faulty LEDs not only prevent the advertising fragment from being switched off, but do not even affect the overall light emission. The vast resources of LEDs practically solve the problems associated with the need to replace them. In addition, LEDs can operate reliably over the widest range of operating temperatures.
Security …
Sometimes, lives depend on the reliability of an object. The use of LEDs in information display devices (road signs, traffic lights, information boards, etc.) significantly improves their visibility and perception. It is no coincidence that many large cities in developed countries no longer have conventional traffic lights, and that LED schemes are used in air and surface navigation systems. Another aspect of the preference for LEDs is their durability and anti-vandal properties. The light sources are made of plastic, making them resistant to mechanical damage. The typical voltage required to operate a single LED is 3-4 volts. Therefore, in conditions where higher safety precautions are needed or high voltage is not possible, LEDs are the best choice. One of the important advantages of LEDs is their resistance to low temperatures.